Research Focus |
|
胰腺癌症类器官-基质平台对T细胞杀伤表现出不同的敏感性 2024-04-29 20:59:30 浏览次数:2700 | |
| 胰腺癌症类器官-基质平台对T细胞杀伤表现出不同的敏感性 来源:仪方生物 www.yeslab.com 胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)的不良治疗反应在很大程度上是由于肿瘤的异质性和影响与肿瘤微环境(TME)中细胞相互作用的免疫抑制性促结缔组织增生性肿瘤基质。因此,迫切需要模型来探测细胞和非细胞串扰的贡献。类器官是有前景的模型系统,有可能产生大量数据,包括表型、转录组学和基因组特征,但仍需要改进模拟TME的培养条件。在这里,我们描述了MatriX(“InterOMaX”)模型系统中与类器官的相互作用,该系统提供了一个基于3D共培养的平台,用于研究基质依赖性细胞串扰。我们描述了其揭示T细胞对小鼠KPC(LSL-KrasG12D/+27/Trp53tm1Tyj/J/p48Cre/+)PDAC细胞以及PDAC患者衍生类器官(PDO)反应的新分子机制的潜力。为此,基于标准化琼脂糖微孔芯片阵列系统设计了癌症细胞的可定制基质和均匀大小的类器官-基质定位,并建立用于与T细胞共同培养和包含基质细胞。我们描述了对T细胞杀伤具有不同敏感性的小鼠和人类PDAC细胞群的检测和正交分析,这在体内得到了证实。通过能够识别和验证T细胞耐药性的候选基因,该平台为更好地了解PDAC中癌症细胞内在耐药性表型的机制奠定了基础。 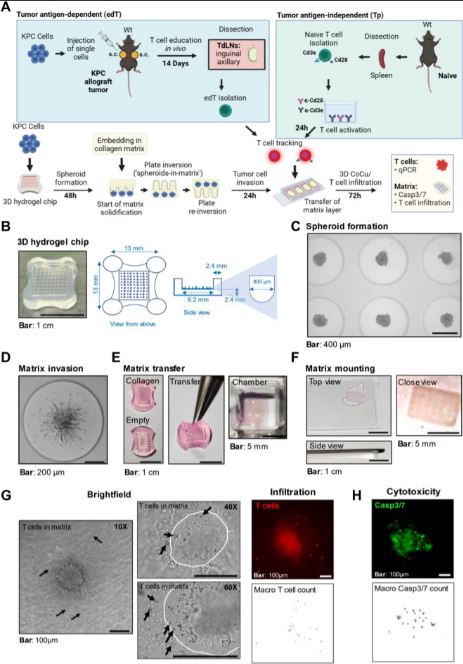    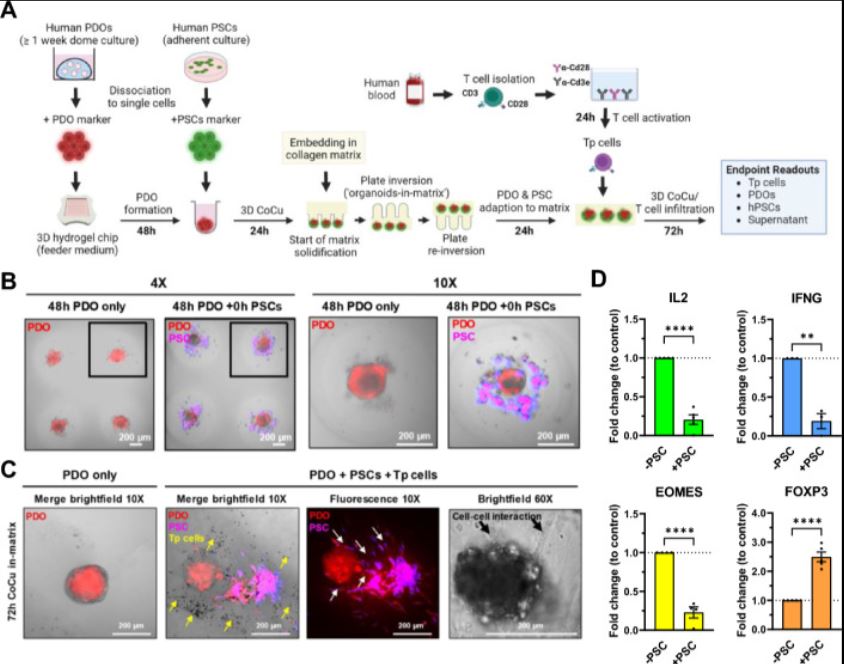 A pancreatic cancer organoid-in-matrix platform shows distinct sensitivities to T cell killing Poor treatment responses of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) are in large part due to tumor heterogeneity and an immunosuppressive desmoplastic tumor stroma that impacts interactions with cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME). Thus, there is a pressing need for models to probe the contributions of cellular and noncellular crosstalk. Organoids are promising model systems with the potential to generate a plethora of data including phenotypic, transcriptomic and genomic characterization but still require improvements in culture conditions mimicking the TME. Here, we describe an INTERaction with Organoid-in-MatriX ("InterOMaX") model system, that presents a 3D co-culture-based platform for investigating matrix-dependent cellular crosstalk. We describe its potential to uncover new molecular mechanisms of T cell responses to murine KPC (LSL-KrasG12D/+27/Trp53tm1Tyj/J/p48Cre/+) PDAC cells as well as PDAC patient-derived organoids (PDOs). For this, a customizable matrix and homogenously sized organoid-in-matrix positioning of cancer cells were designed based on a standardized agarose microwell chip array system and established for co-culture with T cells and inclusion of stromal cells. We describe the detection and orthogonal analysis of murine and human PDAC cell populations with distinct sensitivity to T cell killing that is corroborated in vivo. By enabling both identification and validation of gene candidates for T cell resistance, this platform sets the stage for better mechanistic understanding of cancer cell-intrinsic resistance phenotypes in PDAC. |
